Tech
2023-1954 Evolution of Society and Technology

The years between 2023 and 1954 were a time of profound change, shaping the modern world as we know it. From groundbreaking technological discoveries to shifting societal norms, these seven decades highlight how humanity progressed through resilience, innovation, and unity.
This blog aims to explore the key advancements, events, and trends that defined this period. We’ll take you on a deep-dive into the pivotal moments that reshaped technology, politics, culture, the economy, and more. By the end, you’ll have a deeper understanding of how life in 2023 compares to that of 1954 and what lessons history may hold for our future.
Introduction to the Era: Setting the Stage for 2023-1954
A Snapshot of 1954
The year 1954 marked an era of post-World War II reconstruction and recovery. Countries across Europe were regaining their footing, while the Cold War between the United States and the Soviet Union loomed large. Technology was in its infancy compared to today—TVs were still luxuries, telephones had cords, and computer systems spanned entire rooms.
Socially, gender roles were highly rigid, and much of the world was grappling with decolonization. While health advances were progressing steadily, pandemics and diseases like polio still posed significant risks.
Entering 2023
Fast-forward to 2023, and the world feels almost unrecognizable. Advances in artificial intelligence, renewable energy, and biotechnology dominate headlines. Societal norms are far more inclusive and diverse, and globalization connects us like never before. However, challenges like climate change and the aftereffects of a global pandemic put the human spirit to the test.
Technological and Scientific Advancements
Milestones in Technology
Between 1954 and 2023, humanity witnessed an unprecedented technological uprising.
- 1954 Innovations:
- First Commercial Transistor Radios: Allowed portable music for the first time.
- Nuclear Energy Experiments: The first nuclear power plants were coming to life.
- 2023 Innovations:
- Artificial Intelligence (AI): AI evolved from simple tasks to complex decision-making. Tools like ChatGPT powered communication, education, and industries.
- Space Exploration: From the early Sputnik Satellite to the establishment of Martian research bases by 2023.
Everyday Life Transformation
- Communication expanded from handwritten letters in 1954 to instant global video calls in 2023.
- Healthcare Technology improved dramatically, with wearable health trackers and robotic surgeries becoming the norm.
Socio-Political Landscape
Key Events and Movements
- 1954:
- The Civil Rights Movement gained momentum in the United States.
- Cold War tensions influenced global politics and ideologies.
- 2023:
- Focus on Global Cooperation in addressing climate change.
- Movements around gender equality, diversity, and human rights redefined societies.
Shifts in Governance
From monarchy-led nations transitioning to democracies to the emergence of global summits like the Paris Agreement, the geopolitics of 2023 took a collaborative stance compared to the fragmented world of 1954.
Cultural and Artistic Influences
Highlights of Creative Movements
- Impact in 1954:
- Art reflected post-war anxieties, with the rise of Abstract Expressionism.
- Movies like Rear Window and actors like Marilyn Monroe ruled Hollywood.
- Cultural Shifts in 2023:
- Augmented reality and the metaverse redefined how art and cultural experiences reach audiences.
- Diversity in storytelling enabled the rise of creators across the globe.
Economic Developments
Global Growth Patterns
- 1954:
- The industrial boom focused on rebuilding economies.
- The Marshall Plan helped Europe recover financially.
- 2023:
- Gig economies and digital currencies surged.
- Economic slowdown amid post-pandemic recovery raised questions about economic sustainability.
Key Factors
- The impact of e-commerce drastically reduced reliance on brick-and-mortar models.
- Nations pursued innovation-driven economies fueled by technology and AI.
Environmental and Health Milestones
Sustainability from 1954 to 2023
- Environmental Awareness:
- 1954 was marked by industrial pollution with limited focus on ecological conservation.
- By 2023, greener energy solutions like wind and solar became global priorities.
- Health Transformations:
- From polio vaccines in 1954 to mRNA COVID-19 vaccines in the 2020s, healthcare innovations saved billions of lives.
- Advances in biotechnology, like CRISPR, offered breakthroughs in genetic engineering.
Comparison of Life in 2023-1954
- Daily Life:
- The average person in 2023 has access to technologies 1954 could only dream about, such as electric cars and drones for deliveries.
- Social media has revolutionized how we interact and stay informed compared to the simpler lifestyles of the 1950s.
- Lessons from the Past:
- The recovery and unity shown in 1954 offer hope when facing today’s global challenges.
- Innovations and collaboration have consistently propelled humanity forward, emphasizing the importance of resilience.
You May Also Like: www gravityinternetnet | Reliable Internet Solutions Online
Conclusion
History from 1954 to 2023 teaches us this vital truth—our ability to innovate and adapt helps us overcome every hurdle. Recognizing past achievements and mistakes can guide humanity toward building a brighter, more sustainable world.
Whether it’s learning from 1954’s resilience or 2023’s technological marvels, these years remind us that growth comes from persistence and unity.
Stay curious about history—it holds the blueprint for the future.
Frequently Asked Questions
What was the most significant advancement between 2023-1954?
The rise of artificial intelligence and the internet reshaped technology, communication, and industries globally.
What was life like in 1954 compared to 2023?
Life in 1954 was simpler and less connected globally, with limited technology and traditional societal roles.
What major global events occurred during this period?
Key events include the Cold War, Civil Rights Movement, moon landing, rise of the internet, climate change awareness, and global pandemics.
How did healthcare change from 1954 to 2023?
Healthcare progressed from basic vaccines like polio to advanced biotechnology innovations like DNA editing and robotic surgeries.
What were the most significant cultural changes?
The expansion of diversity, storytelling, and technology-driven cultural experiences like the metaverse marked the later years of 2023.
Tech
The Role of Sensors and Controllers in Laboratory Incubator Performance
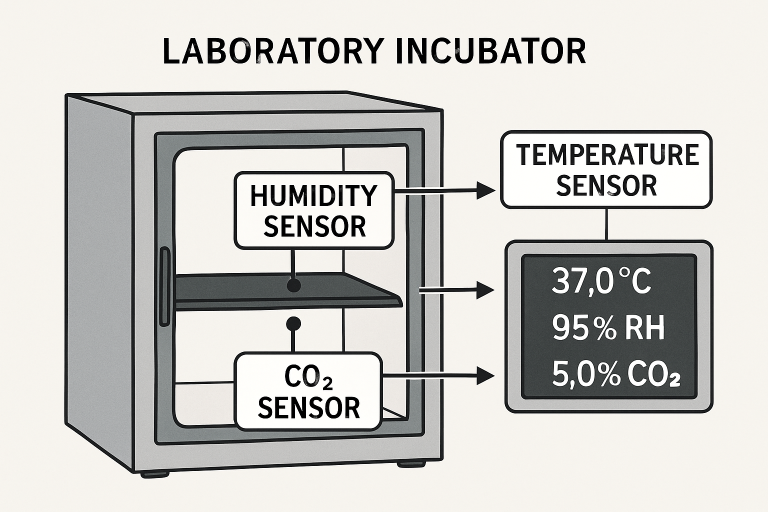
Laboratory incubators serve as the backbone of modern scientific research, supporting the cultivation of cell cultures, microbiological analyses, and numerous experimental protocols that require precise environmental control. Their accuracy and reliability are heavily dependent on the synergy between advanced sensors and nuanced control systems that maintain ideal conditions for scientific work. When these sophisticated machines require expertise, it’s essential to rely on industry professionals, such as those specializing in laboratory incubator repair Delaware, to ensure consistent and dependable performance.
Even minor variations in temperature, humidity, or gas levels within an incubator can compromise the integrity of research. This level of precision, and the mechanisms that ensure it, have been elevated immensely with modern diagnostic sensors and smart automation, setting new standards for reproducibility in laboratory studies. The capability to monitor data remotely and maintain tight tolerances is transforming how laboratories uphold experimental validity, minimize contamination risk, and comply with regulations for sensitive research environments.
Importance of Precise Environmental Control
Laboratory incubators are designed to provide controlled conditions crucial to biological and chemical experiments. Stable temperature, humidity, and gas concentration are fundamental for cellular growth, tissue development, and chemical reactions. Even subtle shifts can introduce variability, impair reproducibility, and threaten the success of high-stakes research such as vaccine development or genetic engineering.
The ripple effect of environmental instability within incubators means risk for cross-experiment contamination and erroneous data—risks that healthcare, pharmaceutical, and clinical research labs cannot afford to take. With ever-tighter regulatory requirements, precise control and reliable monitoring become prerequisites for both research integrity and compliance.
Key Sensors in Laboratory Incubators
Modern incubators rely on an array of robust sensors to continually monitor and regulate key parameters:
- Temperature Sensors: Platinum resistance devices, such as PT100s, are widely adopted for their stability and accuracy, which are essential for protocols that demand exact thermal profiles. These sensors are carefully positioned within the incubator to capture both localized and overall variations in temperature.
- Humidity Sensors: By quantifying relative humidity, these sensors prevent conditions that could lead to sample desiccation or mold growth, which are frequent causes of experiment failure in tissue culture.
- CO₂ Sensors: Accurate carbon dioxide measurement sustains the delicate pH of media in cell culture applications. Advanced photoacoustic and infrared sensors offer reliable CO₂ quantification, accommodating a wide range of research needs.
Advanced Control Systems
The intelligence of an incubator lies within its control systems, which synthesize constant sensor input to adjust environmental outputs in real-time:
- Automated Feedback Mechanisms: Feedback loops operate heaters, chillers, and gas valves with split-second responsiveness, maintaining setpoints with minimal variance. This minimizes manual intervention and human error, thereby strengthening overall experiment reliability.
- PID Controllers: Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) controllers calculate and correct deviations between actual and desired states. This leads to rapid error correction and remarkable environmental stability—critical for sensitive experimental timelines.
Integration of Smart Technologies
The digital transformation of laboratory equipment is changing how scientists interact with their incubators and data:
- Remote Monitoring: Cloud-based interfaces and mobile apps empower researchers to view live parameter data and receive deviation alerts from anywhere, drastically reducing response times and safeguarding research assets. This is invaluable for labs operating under strict quality controls or managing long-duration studies.
- Data Logging and Analytics: Incubators now offer continuous data recording, building a detailed environmental history that supports troubleshooting and advanced data analysis. Laboratories use these insights to optimize protocols and achieve higher reproducibility rates, which are increasingly required for publication in major journals.
Challenges and Solutions
Even with technological advances, practical challenges persist in maximizing incubator performance:
- Sensor Calibration: Sensor drift, caused by environmental exposure or prolonged use, can result in misleading data. Scheduled calibration and proactive maintenance protocols are necessary measures for ensuring ongoing accuracy—especially in labs where regulatory audits are a constant consideration.
- Contamination Risks: The enclosed, moisture-rich environments ideal for cultures are also attractive to contaminants. Solutions such as integrated HEPA filters, antimicrobial coatings, and automated UV sterilization cycles dramatically reduce the incidence of cross-contamination and lost samples.
Future Trends in Incubator Technology
As technology continues to evolve, key trends are emerging in laboratory incubator design:
- Enhanced Automation: Artificial intelligence is being developed to anticipate and respond to environmental changes proactively, thereby reducing human oversight and enabling real-time optimization for even the most sensitive experiments.
- Energy Efficiency: Sustainability is an increasing priority. Newer incubators are leveraging design innovations and material science advancements to reduce energy consumption without compromising performance, helping labs lower their operational costs and environmental impact.
- Improved User Interfaces: More intuitive touchscreens and app-based controls are making incubator operation easier and more accessible, shortening the learning curve for new users and minimizing errors.
Conclusion
Reliable laboratory incubator performance is the result of a sophisticated marriage between advanced sensors and responsive control systems. These innovations empower researchers to maintain exact conditions and focus on groundbreaking discoveries. As digital technologies, automation, and sustainability practices move to the forefront, the future of laboratory incubators promises even greater accuracy, efficiency, and scientific impact.
READ ALSO: Advancements in Battery Testing: Enhancing Safety and Reliability
Tech
Choosing the Right Casters for Your Application
Introduction
Enhancing mobility in equipment—whether industrial machinery, medical devices, or office furniture—relies on selecting the right casters for your specific needs. The process isn’t about picking wheels but finding the ideal match to ensure optimal performance, durability, and safety. Whether you’re retrofitting existing equipment or customizing new projects, understanding how to select wheels for carts is foundational to designing effective solutions for your workplace or facility.
Applications differ widely, and so does the choice of casters. Selecting the correct type and material not only guards against unnecessary wear and tear but can enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs in the long term. Understanding caster fundamentals also helps prevent floor damage and fosters a safer working environment.
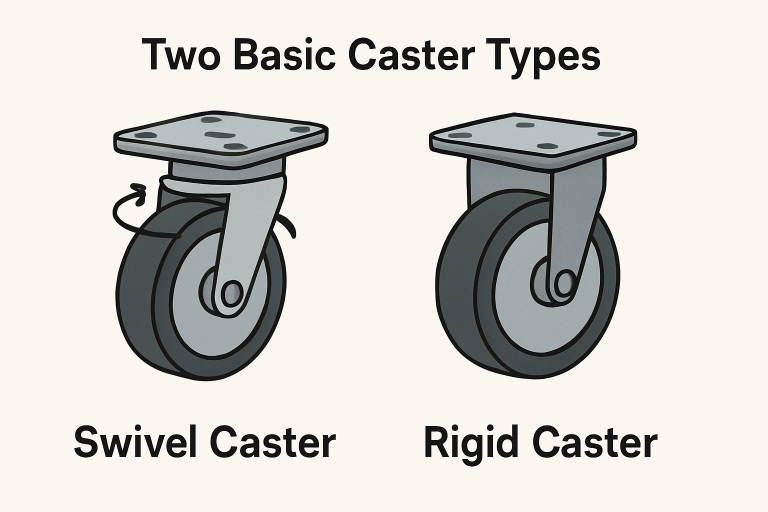
Understanding Caster Types
Casters are designed in two primary categories: swivel and rigid. Recognizing how they function and where they excel sets the stage for further customization.
- Swivel Casters: These offer 360-degree rotation, making them an essential choice for applications where frequent directional changes are necessary, like in hospital beds, rolling tool chests, or restaurant carts, where nimble navigation is critical.
- Rigid Casters: Built to move in only one direction, rigid casters are best for applications that need straight-line stability, such as conveyor equipment or heavy-duty racks that are seldom repositioned.
For many projects, combining both types—swivel on one end, rigid on the other—delivers a blend of maneuverability and stability, accommodating a wide range of operational needs.
Key Factors in Caster Selection
Selecting casters isn’t only about mobility. Some critical elements require careful assessment:
- Load Capacity: Underestimating the weight your equipment needs to support can lead to caster failure, equipment damage, or safety hazards. Always match or exceed the weight guidelines provided by the caster manufacturer.
- Flooring Type: Match the wheel’s composition to your flooring to minimize surface damage. For example, soft wheels are ideal for hardwood, while harder wheels fare better on carpet or concrete.
- Environmental Conditions: Exposure to water, chemical agents, or high heat may necessitate special materials. Neglecting this consideration can lead to corrosion or accelerated wear.
Carefully weighing these factors before purchase ensures that the selected caster will be functional and safe in its environment. For a deeper dive into how workplace equipment can impact safety and productivity, visit this comprehensive overview by Industrial Magazine.
Material Considerations
Material choice influences everything from load rating to the type of maintenance required. Here are the most common options:
- Polyurethane Wheels: Polyurethane is often considered the go-to for multipurpose use. It combines resilience with floor protection, and its resistance to abrasion and chemicals makes it valuable in warehouses and healthcare settings.
- Rubber Wheels: Noted for their quiet, cushioned ride, rubber wheels shine in office environments or on delicate floors but may degrade faster under constant heavy loads.
- Metal Wheels: The ultimate workhorse, metal wheels can bear extreme weights and withstand rough usage. However, they are noisier and can damage floors without proper preparation.
Considering the likely environment in terms of traffic, noise tolerance, and floor quality will help you choose the optimal material for your casters.
Load Capacity and Durability
Load capacity isn’t just the sum of what a single caster can handle; divide the equipment weight (including its contents) across the number of casters, then add a safety factor to allow for uneven weight distribution and shock loads. Overloading casters results in deformation, braking failure, and can present an immediate hazard in busy environments.
Manufacturers provide clear load ratings. Ignoring these guidelines is a primary cause of premature caster failure. Ensure every component is up to the task, especially if mobility is vital for your application’s productivity or safety.
Environmental Factors
The operational setting significantly impacts caster longevity and function. Consider these environmental elements:
- Temperature Extremes: Plastic and rubber compounds may become brittle and lose performance at very low temperatures, while high heat can degrade specific polymers and lubricants.
- Exposure to Chemicals: Industrial cleaning agents, oils, and solvents can rapidly degrade unsuitable wheel materials, leading to splitting or losing traction.
- Moisture Levels: High humidity or frequent water exposure demands corrosion-resistant designs—stainless steel or specialized coatings are preferable in these scenarios.
Factoring in the daily environment ensures longevity and optimal ROI from your caster investment. Machine Design also provides guidance on selecting industrial hardware for challenging environments.
Maintenance and Safety
Routine inspection and maintenance are non-negotiable for any equipment with casters. Schedule regular checks according to the manufacturer’s recommendations. Focus on:
- Checking wheels and axles for wear or cracks.
- Removing any debris or buildup from wheel treads.
- Lubricating bearings and swivels to maintain silent, smooth operation.
Sticking to a proactive maintenance routine extends service life and helps mitigate workplace accidents caused by faulty mobility equipment.
Conclusion
Choosing the correct casters means looking beyond basic functionality to evaluate load capacity, material construction, and the operational environment. Given the array of available options, an informed selection empowers your equipment to deliver optimal utility, protecting your floors, staff, and investment. For more guidance or to shop for quality solutions, explore wheels for carts designed for various commercial and industrial needs.
Tech
Heavy-Duty Mobility Solutions for Industrial Efficiency

Industrial operations rely heavily on equipment and machinery that can withstand demanding conditions while maintaining smooth and efficient workflows. One often overlooked factor in achieving operational efficiency is mobility—how equipment moves, adapts, and absorbs the stresses of daily use. Heavy-duty mobility solutions are designed to support substantial loads while minimizing disruptions caused by uneven surfaces, vibrations, and repetitive motion. Incorporating small shock absorbing casters into industrial carts, platforms, and transport systems can significantly enhance stability and reduce wear and tear, creating a safer and more reliable work environment.
These solutions are particularly valuable in facilities where frequent relocation of machinery or materials is required. By combining robust construction with features like shock absorption, industrial mobility systems help maintain productivity, reduce downtime, and extend the lifespan of equipment. Thoughtful mobility design ensures that operational flow remains uninterrupted, supporting overall efficiency and creating a more ergonomic workspace for employees handling heavy loads.
Advancements in Caster Technology
Recent years have seen a significant leap forward in caster engineering, specifically tailored to meet the needs of heavy-duty applications. Notably, extra-heavy-duty dual-wheel casters are now revolutionizing how plants move their heaviest and most valuable assets. Built for exceptional load capacities, these casters can withstand rigorous industrial use without succumbing to deformation or performance fatigue. Their dual-wheel design distributes weight more effectively, reducing stress on floors and enhancing both maneuverability and long-term durability.
Shock-absorbing mechanisms within modern casters not only protect delicate loads but also contribute to reduced noise and smoother transport. These improvements have enabled facilities to expand their capabilities, allowing them to confidently move precision equipment across varied terrains and tight spaces.
Automated Carousel Systems
Material handling is undergoing a digital revolution, with automated carousel systems at its heart. These systems use vertical or horizontal carousels to optimize space, sort inventory quickly, and automate the movement of parts and equipment. Automating these workflows not only reduces labor costs but also minimizes picking errors and eliminates unnecessary storage space, thereby freeing up valuable floor space for other activities.
Facilities without automation often grapple with workflow interruptions due to manual searching, misplaced goods, or inefficient storage. In contrast, automated carousel systems bring materials directly to workers, improving picking precision while drastically reducing walk time and fatigue.
Digital Transformation in Heavy Equipment
The mobility of heavy equipment is now being redefined not just by mechanical solutions, but also by digital innovation. Connected sensors and software-driven diagnostics empower real-time equipment and asset tracking, allowing teams to anticipate maintenance needs and prevent costly, unexpected breakdowns.
The Role of Digital Twins
One of the most impactful advancements is the adoption of digital twins—data-driven virtual representations of physical machinery. These models are used to simulate, test, and continuously improve processes without interrupting production lines physically. By proactively identifying performance bottlenecks or potential failures, companies can react swiftly and optimize their layouts and workflows to improve efficiency. As businesses leverage these technologies, they not only gain visibility but also actionable insights for continual improvement and cost reduction.
Sustainable Mobility Solutions
With sustainability goals rising to the forefront, eco-friendly mobility solutions are quickly becoming the industry standard. Electrified tuggers, battery-powered loaders, and hydrogen-powered vehicles offer high torque for moving large loads, while also producing far lower carbon emissions compared to their diesel or gasoline-powered predecessors. These systems benefit both the environment and plant economics by reducing fuel and maintenance costs while ensuring compliance with tightening regulatory requirements.
In sustainable operations, the use of recyclable or renewable materials in caster manufacturing, as well as the adoption of low-resistance wheels, is also gaining ground, providing another layer of efficiency by minimizing energy consumption. Beyond the direct savings, sustainable initiatives also help companies attract investment and meet the increasing expectations of eco-conscious stakeholders.
Challenges and Considerations
Transitioning to next-generation mobility systems presents challenges. Initial capital investment can be significant, and staff may require specialized training to adapt to new equipment or automation platforms. Integrating new technologies into legacy systems sometimes necessitates temporary disruptions or phased implementations. Organizations should conduct thorough assessments, pilot projects, and vendor consultations to understand both the short-term impacts and the long-term efficiency gains of such upgrades.
Conclusion
As industrial operations become increasingly complex and competitive, the importance of robust, adaptable mobility solutions cannot be overstated. With advancements in caster technology, the adoption of automated systems, the rise of digital tools, and an urgent shift toward sustainability, manufacturers can achieve safer, smarter, and more sustainable operations. Investing in these innovations not only reduces downtime and operational risk but also positions organizations at the forefront of industrial efficiency and resilience for years to come.
-

 Home Improvement1 year ago
Home Improvement1 year agoEasy Ways to Clean and Maintain Your Foam Play Mat
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoWho Is Andrew Santino Wife? The Full Story
-

 Tech1 year ago
Tech1 year agoExplore iZoneMedia360 .Com Features & Benefits
-

 Entertainment1 year ago
Entertainment1 year agoRemembering Melanie Olmstead Yellowstone’s Unsung Hero
-

 Uncategorized1 year ago
Uncategorized1 year agoPrairie Dog Guide: Habitat, Behavior, and Conservation
-

 Celebrity1 year ago
Celebrity1 year agoA Deep Dive into Jeremy Allen White Movies and TV Shows
-

 Business1 year ago
Business1 year agoHow Influencersginewuld Shapes the Future of Branding
-

 Apps & Games1 year ago
Apps & Games1 year agoThe Pizza Edition Games: A Perfect Slice of Fun and Flavor